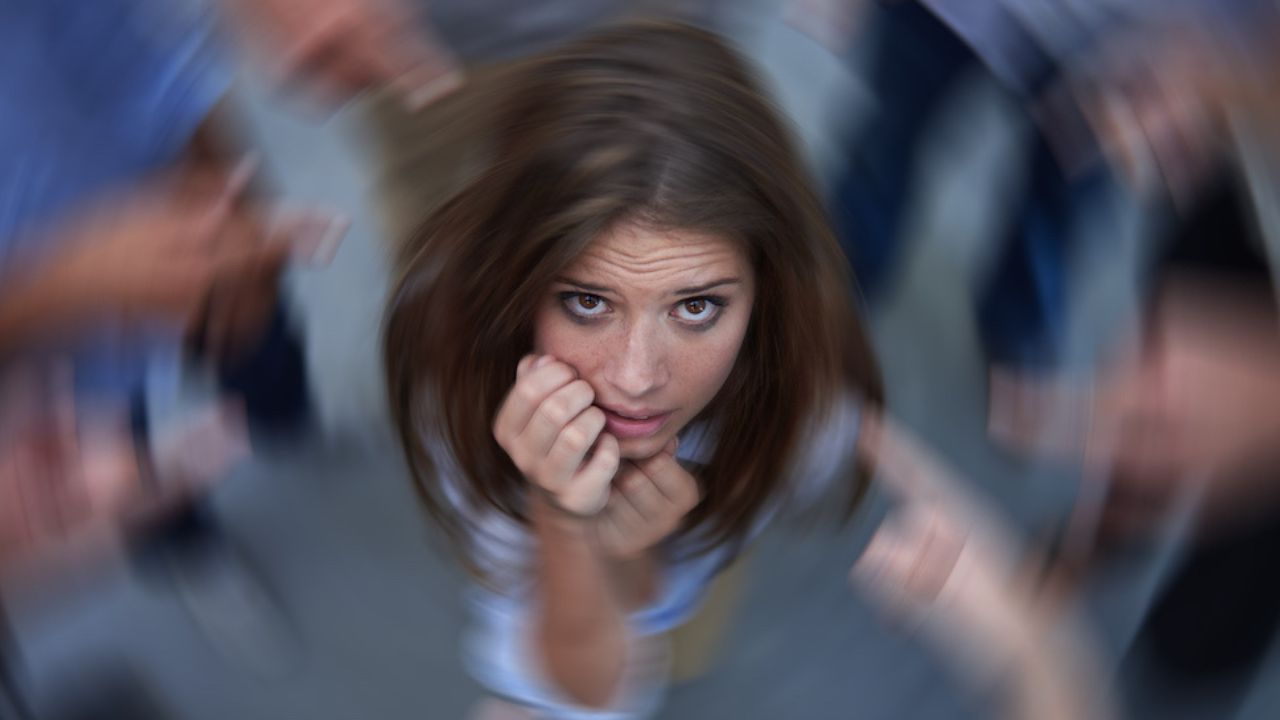
Anxiety is a familiar emotion that everyone experiences from time to time. However, when anxiety becomes a constant companion, interfering with daily life and causing distress, it crosses over into the realm of anxiety disorders. Anxiety disorders, characterized by overwhelming worry and fear, are common yet serious mental health conditions that can significantly affect an individual’s quality of life.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various types of anxiety disorders, their symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options, offering a thorough understanding of these complex mental health conditions.
The Spectrum of Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders are a group of mental health conditions that are marked by excessive and persistent feelings of fear and anxiety. These disorders can manifest in various forms, each with its own unique set of symptoms and characteristics.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
Generalized Anxiety Disorder is characterized by chronic, excessive worry and tension about everyday life events, even when there’s little or no reason to be anxious. People with GAD find it challenging to control their anxiety, often experiencing symptoms most days over a six-month period.
Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD)
Formerly known as social phobia, Social Anxiety Disorder is characterized by an intense fear of social situations due to concerns about being embarrassed, ridiculed, or judged negatively by others. This fear can extend to a broad range of social interactions, leading to avoidance behaviors and potentially resulting in social isolation.
Panic Disorder
Panic Disorder is marked by frequent, unexpected panic attacks that are not tied to specific situations. These panic attacks, characterized by intense fear and physical symptoms such as rapid heartbeat and shortness of breath, can occur suddenly and without warning.
Specific Phobias
A specific phobia is an intense, irrational fear of a specific object, situation, or activity. The fear experienced is disproportionate to the actual danger posed by the feared object or situation, and can lead to avoidance behaviors.
Agoraphobia
People with Agoraphobia experience intense fear of being in places or situations from which escape might be difficult or embarrassing, or help might not be available in the event of a panic attack. This fear can lead to avoidance of such situations, sometimes to the extent of becoming housebound.
Selective Mutism
Selective Mutism is a complex childhood anxiety disorder characterized by a child’s inability to speak in certain social situations, such as school, despite being able to speak comfortably in familiar settings.

Recognizing Anxiety Disorder Symptoms
While each type of anxiety disorder has its unique symptoms, some common signs cut across all these conditions. These symptoms, which can manifest both physically and psychologically, can significantly disrupt an individual’s daily life.
Physical Symptoms
Physical symptoms of anxiety disorders can range from mild to severe, impacting various bodily systems. These can include cold or sweaty hands, dry mouth, heart palpitations, nausea, tense muscles, and trouble breathing. Other symptoms may encompass trembling, dizziness, or feelings of faintness.
Mental Symptoms
On the psychological side, feelings of excessive worry, fear, or impending doom are common. Individuals may also experience panic, nightmares, obsessive thinking, flashbacks to traumatic experiences, and an inability to concentrate.
Behavioral Symptoms
Behavioral symptoms often include avoidance behaviors, where individuals go out of their way to avoid situations or objects that trigger their anxiety. Other behavioral signs may include trouble sleeping, restlessness, and engaging in repetitive, ritualistic behaviors.
Unraveling the Causes of Anxiety Disorders
The exact cause of anxiety disorders remains unknown, but it’s generally believed that a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors contribute to their development. Some potential contributing factors include:
Genetics
Research has shown that anxiety disorders can run in families, indicating a possible genetic link. If a close family member has an anxiety disorder, you may be at a higher risk of developing one.
Environmental Stress
Experiencing stressful or traumatic events can trigger anxiety disorders. Such events can include childhood abuse, the death of a loved one, or witnessing violence.
Brain Chemistry
Changes in the brain’s chemical balance due to prolonged stress may also contribute to the onset of anxiety disorders. Specific areas of the brain that handle fear and emotions may function differently in people with these conditions.
Medical Conditions and Substance Abuse
Certain medical conditions, including heart disease, thyroid problems, and respiratory conditions, can contribute to anxiety symptoms. Additionally, the use or withdrawal of certain medications or illegal drugs can also trigger symptoms of anxiety disorders.
Diagnosing Anxiety Disorders
While there are no specific lab tests to diagnose anxiety disorders, healthcare providers use specific diagnostic criteria to identify these conditions. They will consider the nature, duration, and severity of the symptoms, as well as their impact on daily functioning.
A diagnosis often involves a thorough physical examination to rule out other medical conditions, followed by a comprehensive psychological evaluation. Healthcare providers may use the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) as a reference for diagnosing anxiety disorders.
Treating Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders can be treated successfully using a combination of therapeutic interventions and medication.
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy, also known as talk therapy, can help individuals manage their emotions, thoughts, and behaviors. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is particularly effective, helping individuals identify and change negative thought patterns that lead to anxiety.
Medication
Medications, including antidepressants, benzodiazepines, and beta-blockers, can help manage the symptoms of anxiety disorders. The choice of medication depends on the specific disorder, its severity, and the individual’s response to treatment.
Self-Help Techniques
Engaging in self-help techniques, such as stress management, regular exercise, healthy eating, and adequate sleep, can also help manage anxiety symptoms. Mindfulness techniques, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can also be beneficial.
Living with Anxiety Disorders
Living with an anxiety disorder can be challenging, but with the right treatment and support, individuals can manage their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives. Treatment doesn’t completely cure anxiety, but it can significantly reduce its impact on an individual’s life.
Seeking help when struggling with anxiety is crucial. Early intervention can prevent the condition from worsening and can improve the quality of life. Reach out to a healthcare provider if you or a loved one are experiencing symptoms of anxiety disorders.
Anxiety disorders are common but serious mental health conditions. While they can be debilitating, they are also treatable. With the right treatment approach, individuals can learn to manage their symptoms and lead healthier, happier lives. If you or someone you know is struggling with an anxiety disorder, remember that help is available. Reach out to a mental health professional to start your journey towards recovery.